Brazil’s crypto future: 2026 rules & risks report
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is determined to establish itself as a leader in technology and blockchain. Thanks to its favorable regulatory environment, marked by the creation of the Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) in Dubai, numerous digital currency exchanges and trading platforms have established a presence in the country.

“The UAE’s legal status of cryptocurrencies has paved the way for a thriving ecosystem with several state-level initiatives in Abu Dhabi, Dubai, and Ras Al-Khaimah.”
In this report we examine the cryptocurrency environment in the UAE as it stands today (September 2024) and describe its legal framework. We analyse the crypto market and look at P2P and OTC exchanges in the context of the UAE regulatory environment.
After an initial reluctance to become involved in crypto, the UAE has for some years been making great strides in positioning the country as a leader in the virtual assets industry. The Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) established in Dubai in March 2022 created a favorable regulatory environment, encouraging the establishment of many digital currency exchanges and trading platforms.
The favourable legal environment of the past two years has led to a thriving crypto industry with several (and growing) state-level initiatives in three of the UAE’s emirates, Abu Dhabi, Dubai and Ras Al-Khamiah.
These businesses are bound by strict Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules, ensuring security for customers in an environment of transparency and financial integrity. At the same time, however, over-the-counter (OTC) and Peer-to-Peer (P2P) exchanges are operating beyond regulatory oversight.
Abu Dhabi Global Markets (ADGM) founded.
ADGM introduced cryptocurrency and digital asset guidance (via the FSRA), setting a regulatory framework.
Abu Dhabi launched a global technology system, Hub71, to house startups and investors and boost innovation. By 2023, it announced $2 billion in funding to support Web3 projects.
A dedicated court was set up to hear cases of financial crime.
The UAE adopted a penal code to complement existing AML rules.
The DIFC created the Virtual Asset Regulatory Authority (VARA), the first independent regulator for digital assets.
VARA launched full market product (FMP) regulations after several months during which VARA had granted provisional licenses to Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), enabling them to set up offices and employ staff while not conducting customer-facing business. Next, VARA set up a Minimal Viable Product (MVP) license regime which allowed specific providers to operate in a limited capacity in certain authorized markets only.
The ADGM announced revisions to its AML and sanctions rules and guidance. Changes were made to those provisions which were related to digital assets with the FATF’s travel rule.
The UAE announced the first federal-level regulations governing virtual assets, designed to supervise the industry and protect investors.
The UAE Central Bank issued AML/CTF guidance for financial institutions dealing with virtual assets.
The ADGM announced the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) Foundations Regulations 2023, providing a framework for DLT foundations and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), enabling them to operate and issue tokens.
The DIFC released its Digital Assets Law and the new Law of Security, with amendments to existing regulations, to provide clarity to investors and to keep up with other technological developments.
In recognition of the two years the country had spent improving its financial regulatory framework, the FATF removed the UAE from its grey list.
Source: Cryptoforinnovation.org
The main channels for buying or exchanging virtual assets are direct-access domestic exchange services i.e. Binance, CoinMENA, BitOasis and Rain. There is also an increasing number of P2P exchanges and online marketplaces for specific crypto-redeemable assets such as Binance gift cards.
Telegram, WhatsApp and blogs have become popular avenues for virtual asset transactions beyond the reach of the country’s regulators, including accounts offering P2P services. Many of these groups also provide offers to buy USDT via in-person cash exchanges or bank transfers.
Offshore P2P exchanges including Binance P2P, OKX P2P, and Bitget P2P offer a choice of payment methods, reflecting the differing requirements of their customers. As of today, bank transfers are the most popular payment method.
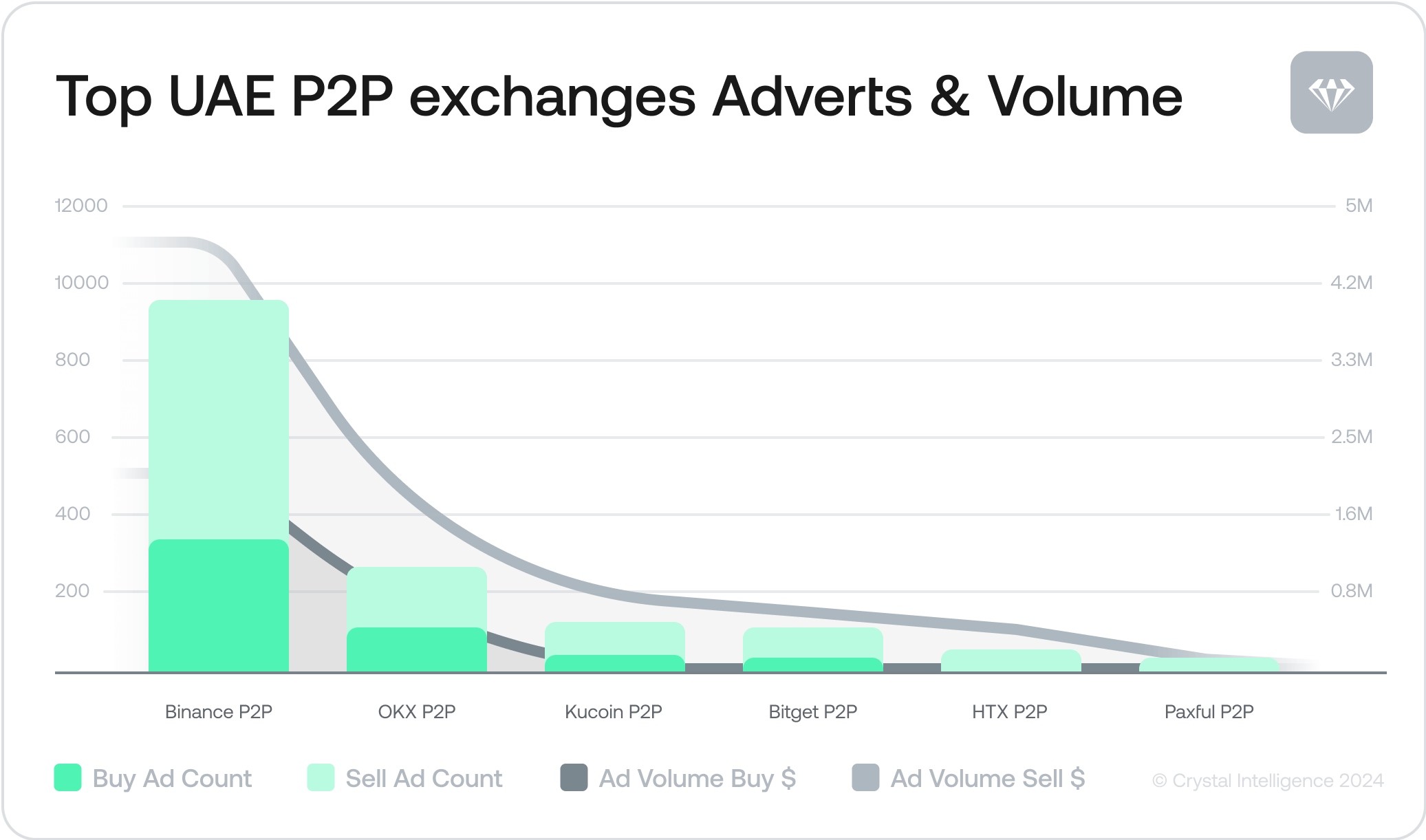
“Up to nearly 1500 adverts on a single day via P2P exchanges aptly demonstrates how dynamic the UAE’s crypto market is.”
The popularity of P2P exchanges is illustrated by the volume of advertising: In a single measured 24-hour period in July 2024, a total of 1,467 adverts buying and selling crypto worth over 10M AED (United Arab Emirates Dirham) were counted:
In the UAE, several Over-the-Counter (OTC) crypto exchanges have emerged, specializing in facilitating face-to-face transactions, particularly renowned for managing substantial cash exchanges. Notably challenging to track, these exchanges provide a discreet avenue for individuals to seamlessly convert large amounts of cash from various currencies into cryptocurrencies and vice versa.
Operating on a discreet level, these OTC exchanges prioritize user privacy and anonymity. One distinct operational characteristic is the utilization of private personal wallets that enhance transaction confidentiality, making it difficult for authorities and Blockchain Analytics tools to identify them.
OTC exchanges in the UAE cater to high-volume transactions, attracting both individual and institutional investors seeking to conduct sizable trades in fiat currency for cryptocurrencies and vice versa. The direct, face-to-face nature of these exchanges fosters transparent communication and negotiation, establishing a heightened level of trust among participants.
By requiring cryptocurrency companies to obtain licenses and comply with regulatory obligations, the UAE is taking a proactive step towards managing these risks while fostering innovation and growth in the industry:
All VASPs that are licensed by VARA must follow four compulsory rulebooks:
VARA also developed seven activity-specific rulebooks to address the risks associated with the operations of virtual assets:
Find out more about the UAE’s regulatory landscape here.

Instances of illicit activities that accept crypto assets for payment, including prostitution services, gambling groups, and drug dealer scams, have also been identified:
Get detailed analyses of criminal activity in the UAE’s crypto industry and case studies by contacting us here.
Unregulated OTC and P2P exchanges pose significant risks to the UAE. While they prioritise privacy and convenience for both vendors and customers, they avoid supervision and oversight, thus enabling criminal activity and escaping the UAE’s VA regulatory and supervisory framework and breaking the law.
Get detailed analyses of risk factors in the UAE’s crypto industry by contacting us here.
They link to WhatsApp accounts, mostly with Pakistani and European mobile numbers, where a customer can inquire and pay via Easypaisa (a Pakistani money transfer app) and the “exchanger” transfers the pre-agreed cryptocurrency to the customer’s wallet.
There is a growing trend among several companies and developers who are accepting cryptocurrencies in exchange for goods. Crystal identified:
Get detailed analyses of crypto uptake in the UAE’s business sector by contacting us here.

The UAE’s progress in its crypto regulation journey was best expressed by its removal from FATF’s grey list in April 2024. The impact of improved AML/CFT regulation and compliance is also seen in the uptick of crypto businesses and dealers moving their operations to the UAE to enjoy its safe and accommodating virtual asset legal framework. If the risks described in this report are constantly addressed, the next step for the UAE is to harmonize crypto regulation throughout the Emirates.
To learn more about how Crystal can help you navigate the evolving crypto industry landscape, please book a demo here.

Investigations | February 26, 2026
Mobile wallets account for 45-85% of crypto settlement in emerging markets. Our research traces the flows and documents the compliance gap regulators

Market Analysis / Research | February 24, 2026
Major stablecoins face transfer declines as alternatives gain momentum. USDT drops 21%, USDC falls 13%, while USD1 rises 67% to $104.9M daily.

News | February 18, 2026
Brazil weighs $68B BTC reserve; Hong Kong grants rare license to VDX; Poland revisits vetoed crypto bill.