Learn how an AI-assisted deepfake ID document provider popular in Iran, is being used to bypass KYC protocols on crypto exchanges worldwide. Find out what risk this presents to crypto exchanges.
Deepfake algorithmic ID’s: a new frontier of crypto fraud
The rise of deepfake artificial intelligence (AI) tools used, in this instance, by a fake KYC document provider to synthesize convincing identification documents is flourishing in Iran. The illicit service is popular with Iranian customers seeking to access the international crypto market, creating yet another challenge for cryptocurrency exchanges globally.
To understand what this service is, why the risk environment it flourished in developed, what those risks are, and how to protect your organization against them, read on.
What is a deepfake ID in crypto?
One service openly advertises its services through its professionally veneered website, stating that it “provides authentication services, free static IPs, and open-layer files for Iranian users and sanctioned platforms with 5 years of experience and specialized support.”
Meanwhile, the deepfake tool exploits cutting-edge AI technology to circumvent crypto exchanges’ know your customer (KYC) processes. The tool can, in some cases, outsmart facial recognition and other biometric identification techniques used by crypto exchanges via an app to create fake passports, drivers’ licenses, identity documents and such. The high-tech, AI-driven fake product has proved convincing enough for in-country Iranians to bypass KYC and create illicit accounts on crypto exchanges.
Crystal Intelligence’s investigations team employed its special skillset to learn more about how it works and the risks it poses to the onboarding processes of legitimate crypto exchanges. Some key takeaways follow.
Firstly, there is the professional and welcoming website landing page:

It also offers different planoptions:

A risk factor to crypto exchanges is how effective the deepfake identity documents are. In the example below, a fake ID was used to successfully bypass KYC procedures on a large exchange:
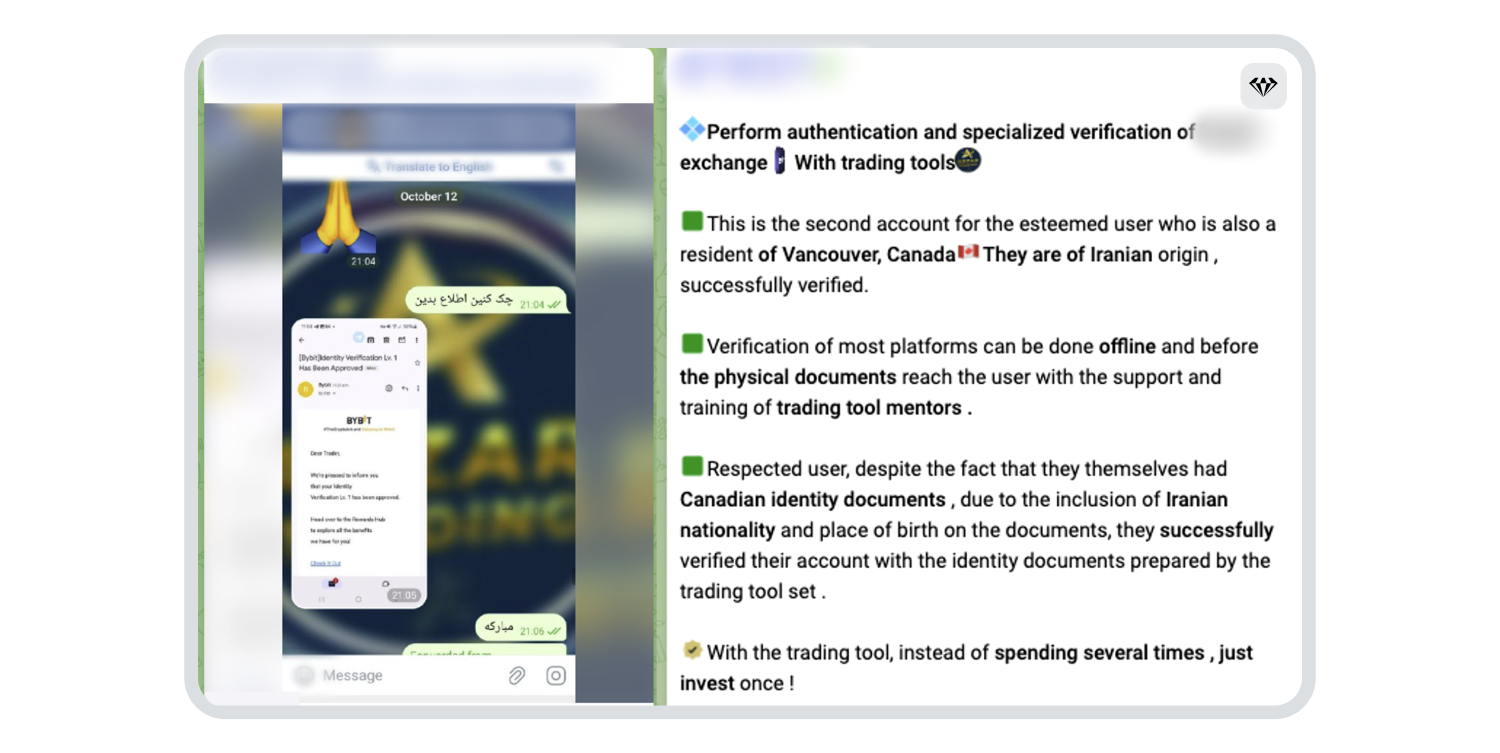
Additionally, the service is sufficiently sophisticated and brazen enoughto offer a post-sales customer service option, and keep users informed via their social media channels about platforms where bypassing KYC can be tricky. The service even advises them to contact the customer support teamwhich assistswith successfully completing KYC on such platforms, such as in the example below:
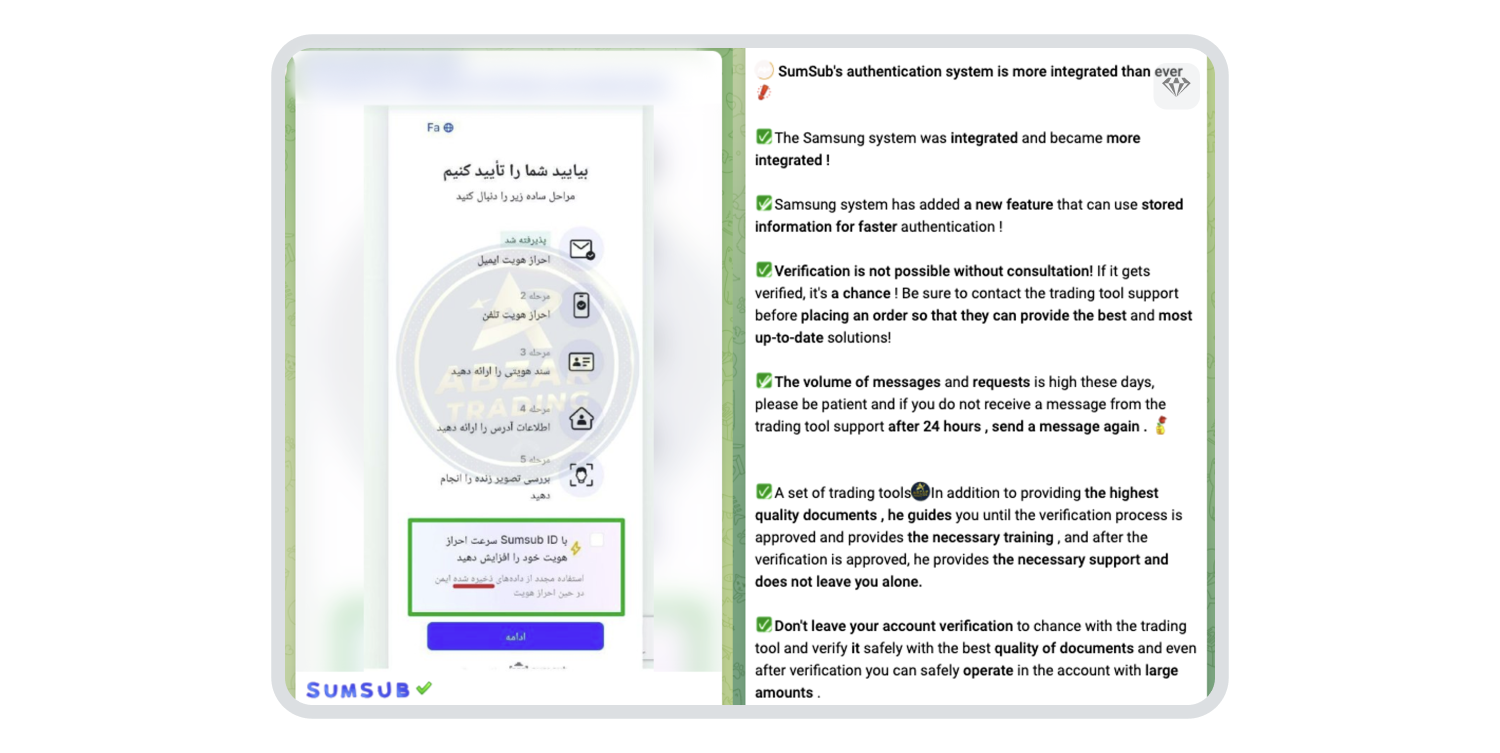
They also issue warnings against using cheap alternatives for duplicate IDs, as in the example below:
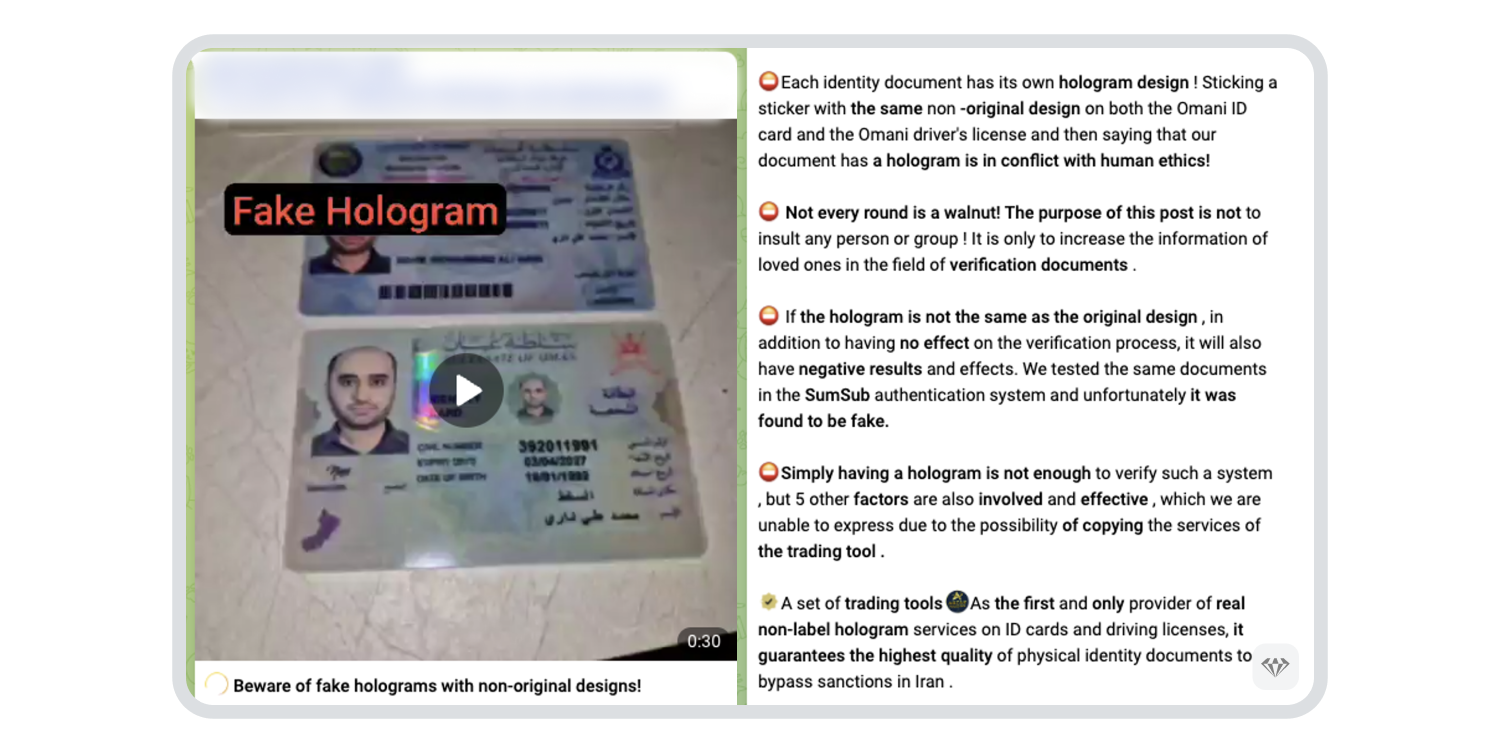
While Crystal is focused on the risks of such services, it is important to understand the context in which Iran has adopted this technology with such enthusiasm. To find out, read on.
Why sanctions have created an ID fraud boom, and the Iranian crypto industry
While some 15 to 19 million Iranians reportedly participate in the crypto industry, Iran’s strained geo-political status in the world presents challenges for the crypto industry and Iranian residents wishing to trade in digital currencies. This is no small number, representing almost 20% of the population who are engaged in cryptocurrency activity.
Drivers such as a weak national currency (Iran’s rial is among the most inflated in the world, at around 45% in 2023) and a lack of access to international financial systems due to sanctions make it fertile ground for cryptocurrency adoption.
Additionally, with the Iranian diaspora of over four million as of 2019 financially cut off from their homeland and families by much of the traditional finance system, cryptocurrencies had offered an alternative cross-border remittance system which is now more hamstrung by sanctions than ever before. This provides another incentive for seeking fake foreign IDs to bypass KYC vetting on exchanges.
International Pressure on Iran continues to mount
The United Nations (UN) continues to implement sanctions—which have been in place in some or other form for several decades— against Iran concerning issues related to the proliferation of nuclear weapons, arms trading, and terrorism financing. Meanwhile, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) currently has Iran on its blacklist for similar reasons.
The US Government’s State Department has also long sanctioned Iran, and some local crypto exchanges are suspected of dealing with the country’s government, the prime target of these sanctions. Ironically, the raft of sanctions imposed during 2017 are reported to have galvanized the growth of Iran’s domestic crypto exchanges, including the largest, Nobitex, which has almost 6 million active users.
The effect on the world’s crypto exchanges of contravening these sanctions and knock-on effect on Iran’s crypto industry is immense. In November 2023, Binance reached a plea agreement worth $4B in total with the US Department of Justice (DOJ) for, among other things, violating US sanctions by making almost $900M in trades with Iran-based customers from January 2018 to May 2022.
Binance responded by creating and adding Iran to its list of prohibited countries. Several other major exchanges have also heeded the risk of violating US sanctions by excluding Iran, including ByBit and MEXC. This additional isolation of in-country Iranians from the international crypto community has further shut them out of the global industry when they are identified as such.
Why sanctions impact deepfake ID fraud in Iran’s crypto industry domestically
In May 2024, suspicions arose that Nobitex was collaborating with the Iranian government to violate sanctions. These culminated in blockchain analytics platform Arkham Intelligence publishing Nobitex’s wallet information on its publicly available explorer, as well as Codatta – another platform – launching a bounty program to identify wallet addresses linked with Iranian exchanges. This highlighted the activity of Iranian exchanges to a wider audience, a matter not lost on Iranian users. The below interaction on X speaks to the frustration some Iranians feel about the fallout from the roadblocks put up for Nobitex customers:
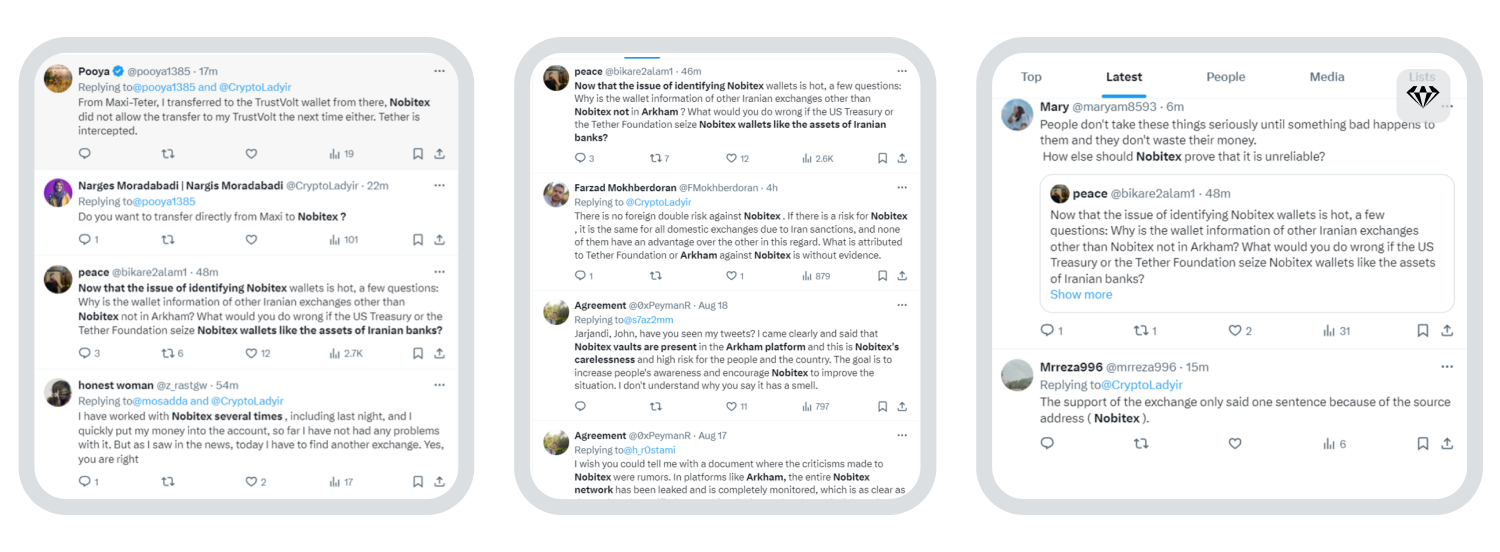
The Codatta position on wallet label ‘bounty hunting’, below:
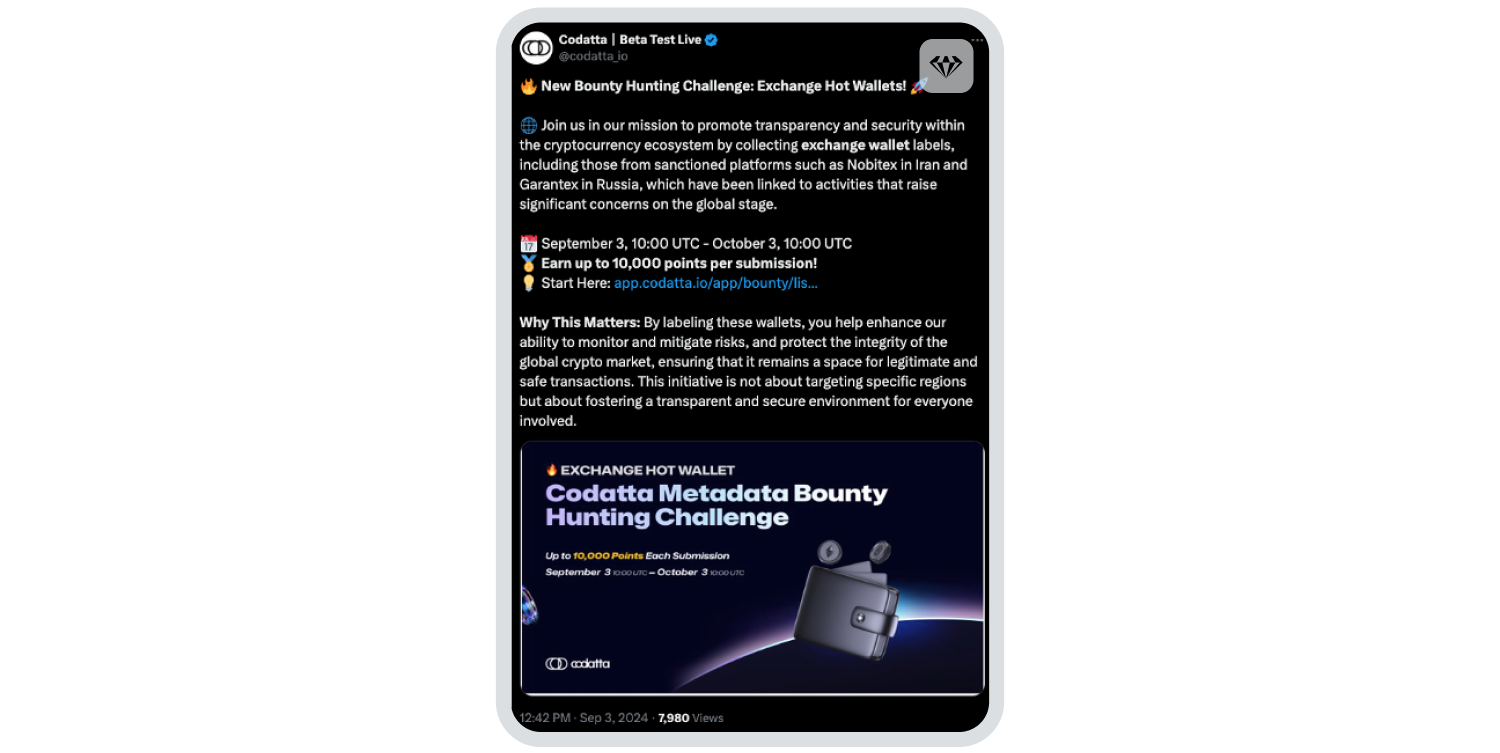
Other factors impacting Iranian Crypto Users
The instability, conflicts—and concomitant fluctuations in the Iranian RI’s value — of the geographical region and political climate also impact Iranians’ access to their digital assets. With the sanctions regimes already in place and greater tensions following the October 1, 2024, missile attacks by Iran on Israel, some Iranians have struggled to access their funds even in domestic exchanges.
The consequential economic impact of the regional conflict has further weakened the rial. To prevent instability, the Iranian government restricted fiat payment network Shaparak’s access to crypto platforms, limiting rials to crypto conversions.
See below:
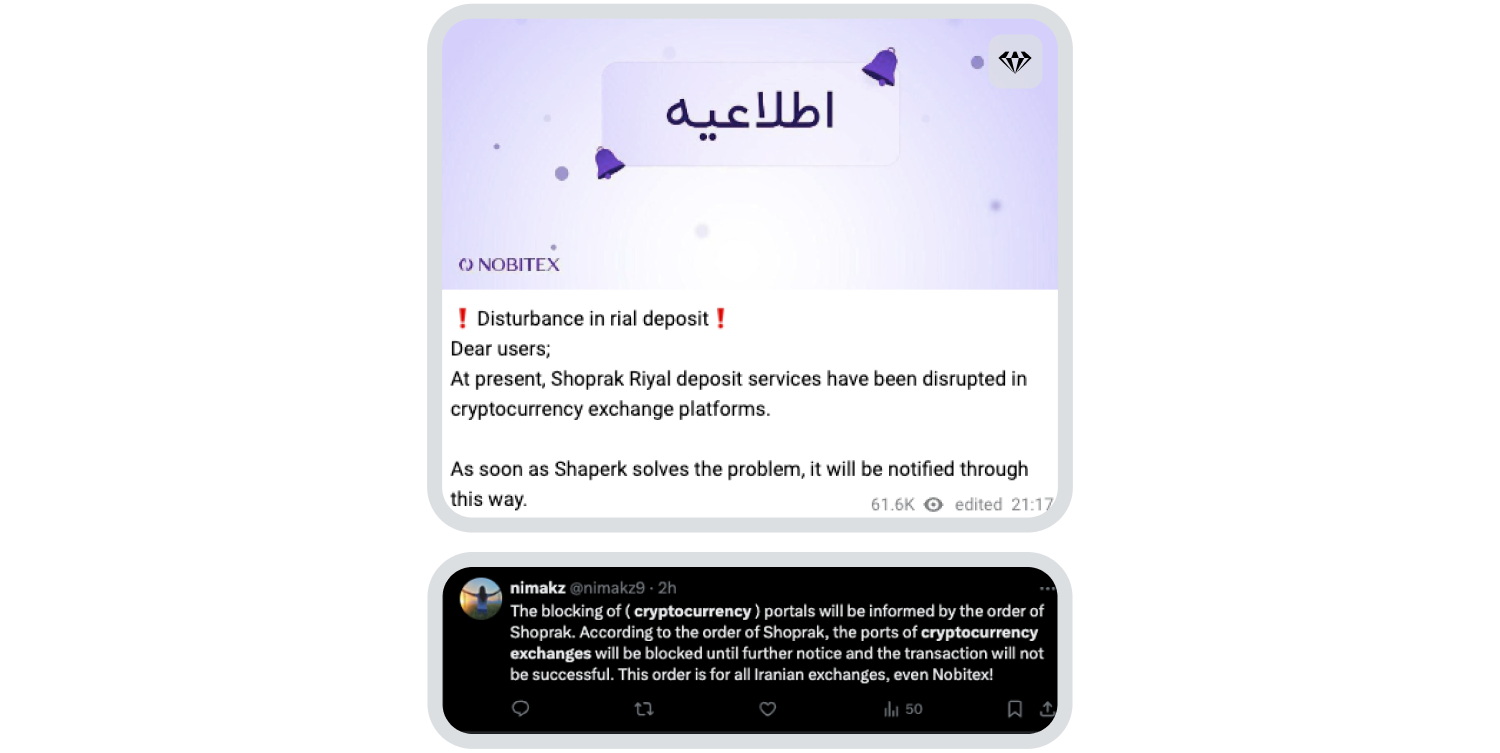
What risk do fake ID services pose to crypto exchanges?
The context provided has tilled fertile ground for entities to offer deepfake documents to Iranians wanting to dodge the sanctions impeding or preventing them from trading crypto internationally by getting foreign identities.
Furthermore, the rapid advancement and growing popularity of AI technology has made it more accessible, easier to use, and cheaper to acquire, widening the market base for illicit activities.
With little clear progress in the broader context of Iran’s political or economic status, it is important that crypto exchanges be vigilant of ongoing and evolving deepfake scams to avoid criminal liability, colossal financial penalties for sanctions violations, and reputational damage.
How can crypto exchanges protect themselves from deepfake ID fraud?
In the context of dealing with ID fraud, several protective measures stand out:
- Improve, adopt, and implement AI-based tools to scrutinize KYC documents and compare them with existing government or law enforcement databases.
- Insist on multiple levels of biometric identity verification, such as interacting with the subject (speech, instruct head movements or blinking), and add in fingerprint and voice testing.
- Be vigilant in or avoid high-risk and high-risk adjacent jurisdictions and be vigorous in compliance with regional regulations and international requirements.
- Implement tough and ongoing monitoring and evaluation protocols which, ironically, employ AI to detect fake IDs during customer due diligence (CDD) and KYC procedures. This includes implementing the Travel Rule and, critically, inculcating effective and ongoing account monitoring.
What does the future of AI-driven ID fraud hold for crypto?
While the global data platform, Statista, projected that the worldwide cryptocurrency market revenue is set to reach $56.7B in 2024, Price Waterhouse Coopers reported that AI has the potential to contribute $15.7T to the overall global economy by 2030.
Against this backdrop, the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)warnedthe financial sector about the threat of AI-augmented ID fraud in November 2024. The FBI repeated the caution in December.
Such predictions and warnings indicate that the threat is not unique to Iran. Accordingly, crypto businesses will have to pre-empt where possible and adapt as necessary.